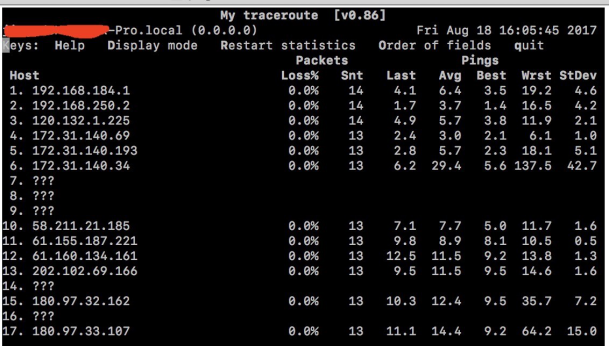
Troubleshooting
Use mtr to troubleshoot network anomalies
The main functions of the mtr tool are twofold: troubleshooting abnormal points during packet loss and collecting paths. It is a combination of ping and tracert. Compared with ping, it can display routing nodes, and compared with tracert, it can show the packet loss situation of intermediate routing nodes. Based on the packet loss gradient, one can simply analyze the possible abnormal nodes and provide feedback to the corresponding operator.
Due to the possible asynchronous routing and ECMP in the backbone external network path, it is recommended to provide two-way mtr results.
(Asynchronous routing: It means that the forward and reverse paths of data packets are inconsistent. There may be no obvious abnormal points in one direction, while abnormalities may only appear in the other direction.
ECMP: Internet service providers perform load balancing across multiple paths. If one of the paths malfunctions, it can lead to packet loss for some IP addresses.)
Use mtr on Windows
Usage (take winmtr as an example)
1、Enter the target domain name or IP address (make sure not to add a space before), and click “start” to begin detection.
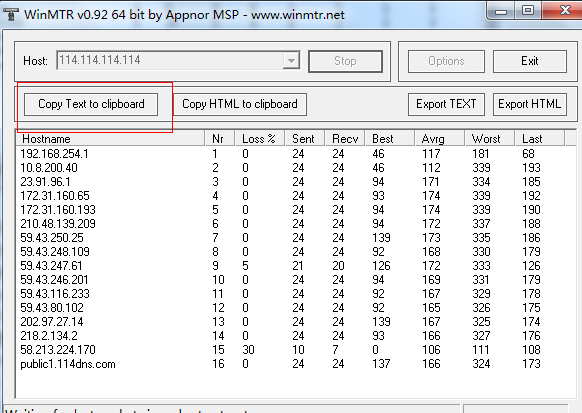
2、 After running for a while, click “stop” to stop the detection. You can also select “Copy Text to clipboard”: to copy the test results in text format to the clipboard.
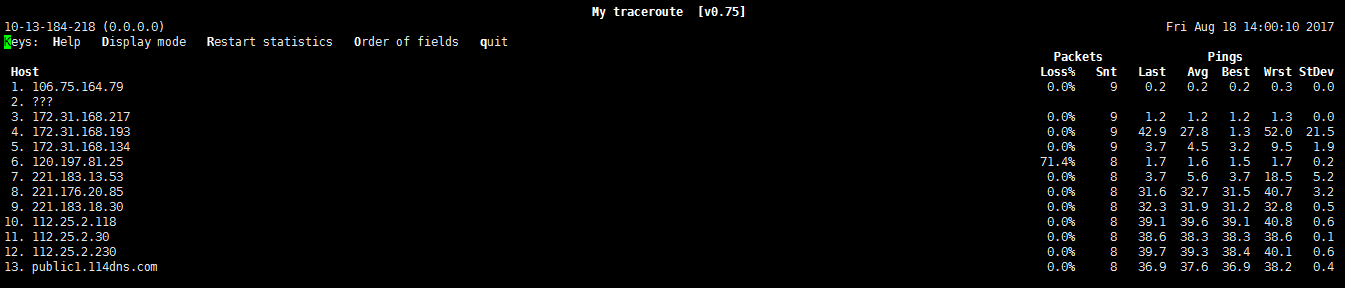
Use mtr on Linux
Download and installation
For centos system, you can use “yum install -y mtr” to install. Other operating systems are recommended to use relevant download tools.
Usage
1、Enter “mtr + target domain name or IP address”, and press “enter” to execute the command.

2、Wait for the route trace to end.
Use mtr on Mac
Usage
1、Enter “mtr + target domain name or IP address”, hit “enter” to execute, and wait for the route trace to end.