Content Forwarding
Listeners support matching domain names or access paths according to content forwarding rules, and can forward matching requests to specific hosts in the backend, for fine management of backend service nodes. Content forwarding rules are divided into “domain forwarding” and “path forwarding”. Both of the forwarding methods can use regular expressions that comply with PCRE rules to describe, such as “www.[123].demo.com ”, “..demo.com” or “/path/img/..jpg”. When creating a rule, the rule content cannot be empty and cannot contain escape characters.
Add Content Forwarding Rules
By default, there will be one Default rule strategy. This strategy takes effect when all requests fail to match successfully and will be matched to the Default rule for forwarding.
- Log in to the ALB console.
- In the top menu bar, select the region of the ALB instance.
- Choose one of the following methods to open the listener configuration.
- On the Instance List page, click Listener Management in the Operation column of the target instance.
- On the Instance List page, click the target instance ID or details. On the Listener Management tab, enter the listener details page.
- In the Listener Details page, select the Content Forwarding tab.
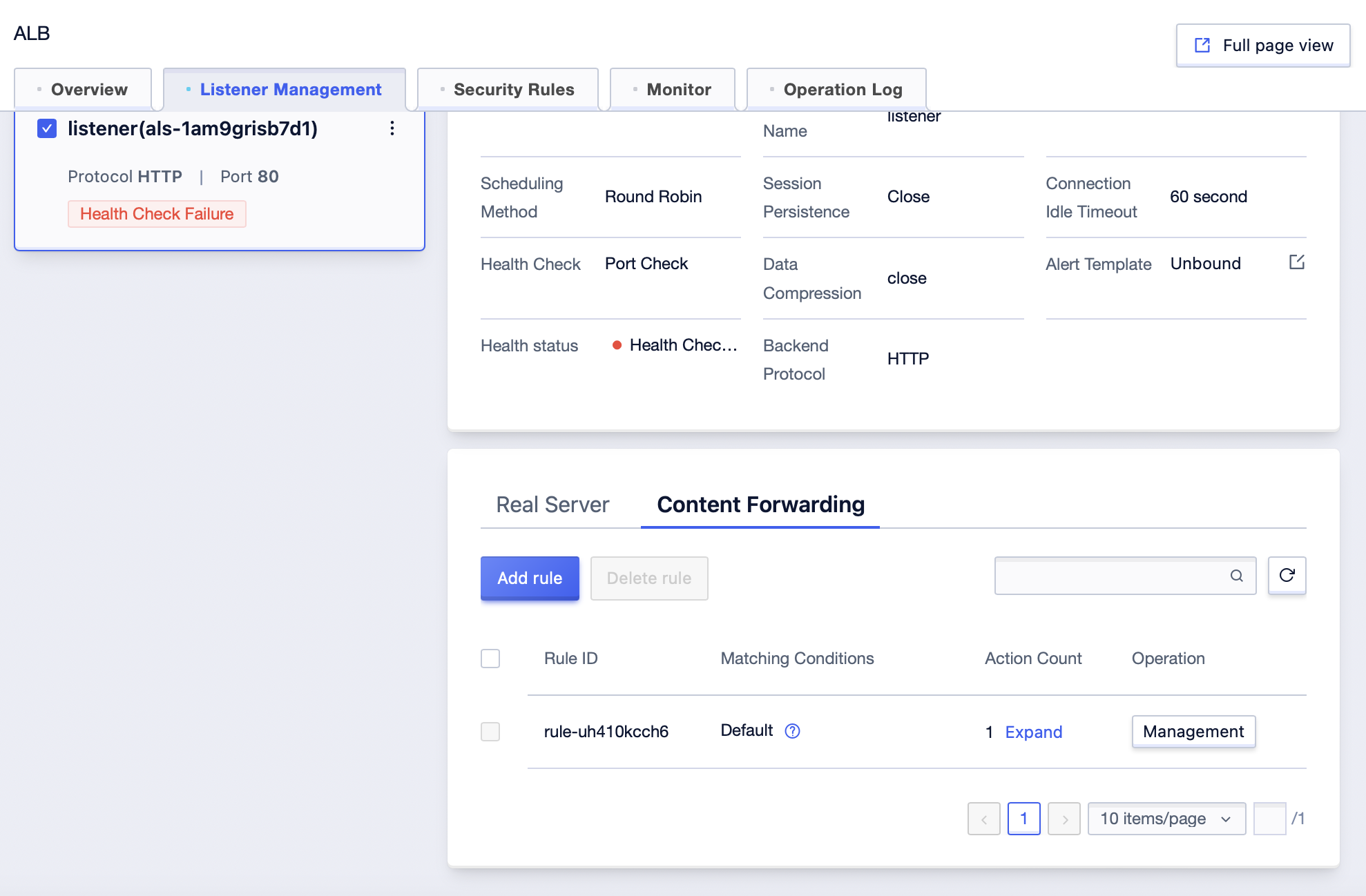
5. Click “Add Rule” in the upper left corner, and edit the following content on the rule addition page.
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| Forwarding Type | Domain Forwarding | The length of the forwarding domain is limited not to exceed 255 characters, and the single-level length not to exceed 63 characters. The regular expression supports Chinese, letters, numbers and special characters, including - ? = ~ _ - + ^ * ! $ : & | ( ) [ ] . (”:” can only be used in the form of adding a port after the domain name, and it is used in non-80 port HTTP and non-443 port HTTPS scenes.) The wildcard domain name supports Chinese, letters, numbers and special characters, including . : * _ - . _ Cannot be put at the beginning or end. Wildcard domain names currently only support * . Or . at the beginning or . * or . at the end, and * can only appear once in a single domain name. |
| Path Forwarding | 1-255 characters. Support Chinese, letters, numbers and special characters, including . - _ / = ? ^ * $ ! : ( ) [ ] + | | 1-255 characters. Support Chinese, letters, numbers and special characters, including - _ / = ? ^ * $ ! : ( ) [ ] + | |
| Forwarding Conditions | Regular | Support regular expressions. For example: www.[123].demo.com can match www.1.demo.com 、 www.2.demo.com 、www.3.demo.com and other domain names. |
| Wildcard | Support wildcard matching, For example: .demo.com or .demo.com can match all domain names ending with demo.com, www.demo . or www.demo . can match all domain names starting with www.demo . /path/img/.*.jpg can match all files ending with jpg under the /path/img/ path, such as /path/img/demo.jpg, /path/img/1/demo.jpg, etc. | |
| Custom Actions | Write a Header: Enter the key and branch content, which will overwrite the existing header variables in the request. Delete a Header: Select the Header to be deleted. It supports deleting key-value pairs in the request Header, including headers such as X-Real-IP, X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Proto, and X-Forwarded-SrcPort. Cross-Domain: When any one of the protocol, domain name, or port of the request URL sent by the client is different from that of the currently returned page URL, it is considered a cross-domain request. Requests include simple requests and pre-check requests. Allowed Cross-Domain Access Sources: Set the sites that are allowed to access the service resources through the browser. Allowed Cross-Domain HTTP Methods: Select the HTTP methods allowed for cross-domain access, including GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, and PATCH. Allowed Cross-Domain Headers: In addition to the basic headers built into the browser, set the headers allowed for domain access. Exposed Headers: The response headers that are allowed to be accessed by the browser and JavaScript scripts. Whether to Allow Carrying Credentials: Whether to allow carrying credential information during cross-origin access. Values: Allowed or Not Allowed. By default, it is set as Allowed. Browser Cache Time: For pre-check requests, set the maximum cache time of OPTIONS pre-check requests in the browser. Unit: seconds. Value range: -1~172,800. | |
| Final Actions | Forward To: Select the target node from the service node list. Return a Fixed Response: Enter the response status code, and then select to fill in the response body. The response status code must be a numeric string in the 2xx, 4xx, or 5xx range, where x can be any digit. |
6. Click “Confirm” to complete the configuration of the content forwarding rule.
Manage Content Forwarding Rules
After adding a content forwarding rule, you can edit the node or action associated with the current rule.
- Log in to the ALB console.
- In the top menu bar, select the region of the ALB instance.
- Choose one of the following methods to open the listener configuration.
- On the Instance List page, click Listener Management in the Operation column of the target instance.
- On the Instance List page, click the target instance ID or details. On the Listener Management tab, enter the listener details page.
- In the Listener Details page, select the Content Forwarding tab to enter the Content Forwarding page.
- Select the content forwarding rule you want to edit, click Management in the operation column, and enter the rule editing page.
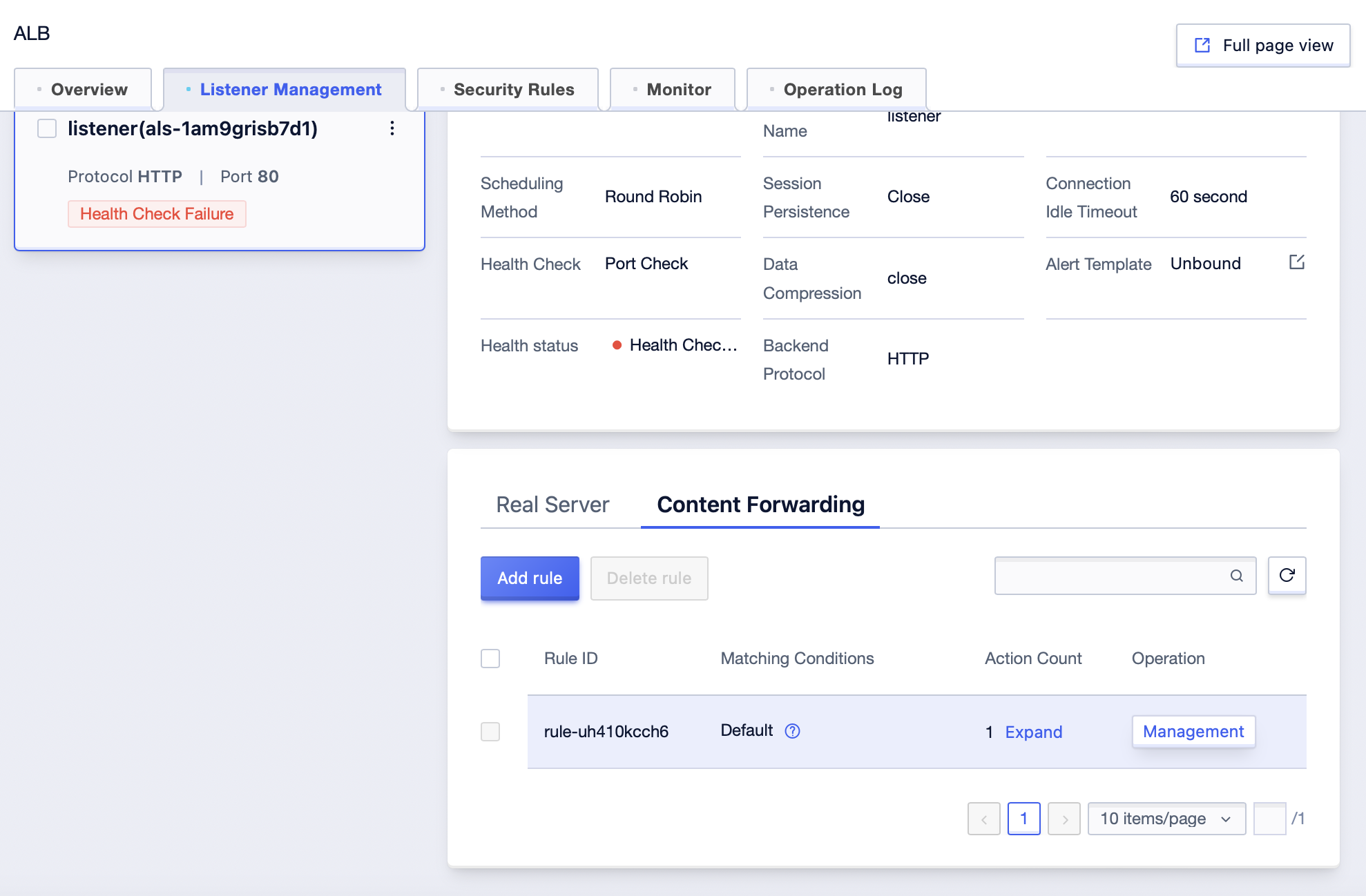
6. You can edit the forwarding type, forwarding content, and actions of a rule.
Delete Content Forwarding Rules
After adding a content forwarding rule, you can edit the node or action associated with the current rule.
- Log in to the ALB console.
- In the top menu bar, select the region of the ALB instance.
- Choose one of the following methods to open the listener configuration.
- On the Instance List page, click Listener Management in the Operation column of the target instance.
- On the Instance List page, click the target instance ID or details. On the Listener Management tab, enter the listener details page.
- In the Listener Details page, select the Content Forwarding tab to enter the Content Forwarding page.
- Select the content forwarding rule you want to delete.
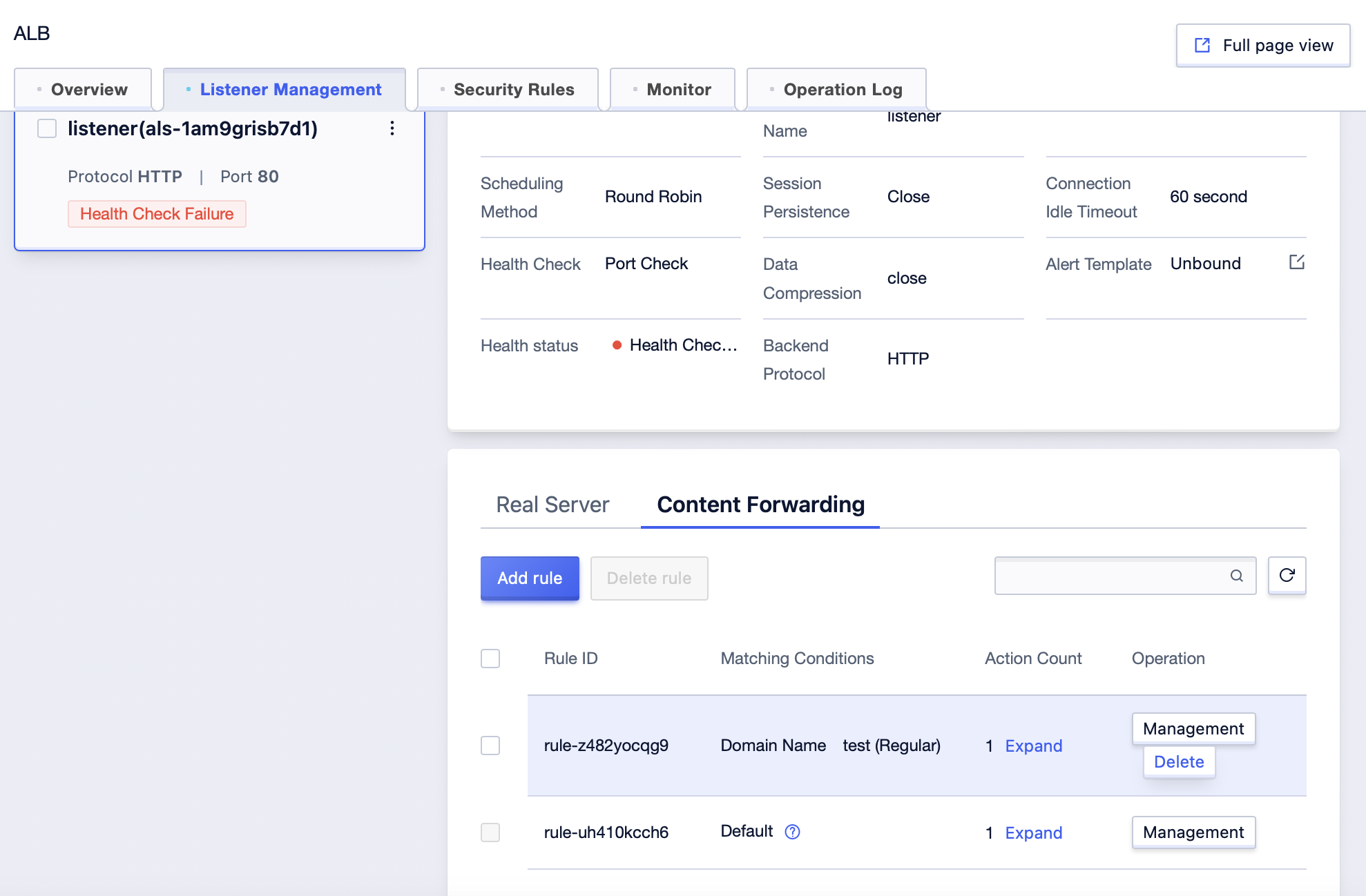
6. Click “Delete” in the operation column, or click “Delete Rule” in the upper left corner.
- In the rule deletion confirmation pop-up, click “Confirm” to delete the rule.
Match policy
Forwarding rule priority: The matching policy is sorted according to the time the forwarding rule is added. The priority is from high to low, and the later the rule is added, the higher the priority.
If the same domain name is configured in different forwarding rules, the rules with the same domain name will be aggregated and matched and forwarded according to the highest priority rule set by the domain name.
If the request matches the domain name, but the rule does not configure the request path information, then the ALB will return 404 to the client.
Default forwarding rule: After creating the listener, the system will automatically create a default forwarding rule. This forwarding rule matches all client requests; it is forwarded to the set backend service node.
Description of the default forwarding rule: The default forwarding rule cannot be deleted and you can change the backend service node for forwarding. The priority of the default forwarding rule is the lowest.